Fundamentals of Firefighter Rehabilitation
In the past, firefighter rehabilitation at an emergency incident was recommended. With the creation of NFPA 1584: Standard on the Rehabilitation for Members During Emergency Operations and Training Exercises, firefighter rehabilitation became a standard of care.
From a health and safety perspective, we cannot overemphasize the importance of establishing a rehabilitation sector at every emergency incident and training exercise where members physically exert themselves. This includes (but is not limited to) emergency incidents involving fire suppression, rescue, E.M.S., and hazardous materials.

The primary purpose of firefighter rehabilitation is to provide mitigation and recuperation of physical, emotional, and physiological stress which are incurred from any emergency incident or training. Aside from helping recuperate our energy and performance, rehabilitation has been shown to decrease the incidence of firefighter injury and death.
After the incident commander has established and assigned the rehab sector to an appropriate unit, two main objectives need to be completed while firefighters are in rehab: Medical Monitoring and Required Actions.
Firefighter Medical Monitoring
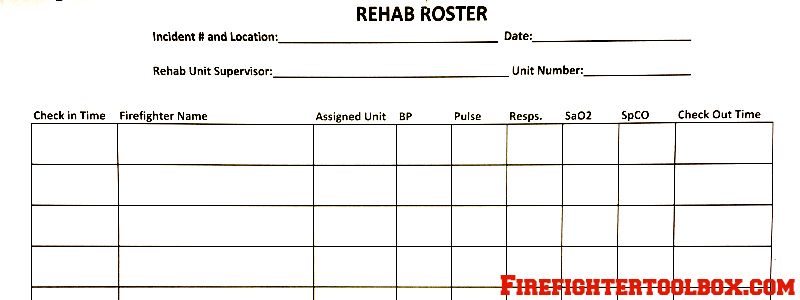
The unit performing rehabilitation will obtain and document the following information from each firefighter:
- Check-In Time
- Firefighter Name and Assigned Unit
- Vital Signs (2 Sets): Blood Pressure, Pulse, Respirations, SpO2 (% of oxygen), SpCO (% of carbon monoxide), and Temperature
- Cardiac Monitoring if the firefighter is symptomatic or has abnormal vital signs
- Check-Out Time

Masimo Rad-57: This device can monitor heart rate, oxygen levels, and carbon monoxide levels found in the blood.
Required Actions For The Rehab Sector
If we are responsible for the rehab sector, we can perform the following actions:
- Locate the Rehab area in a relatively controlled environment where firefighters can sit down to rest.
- Removal of firefighters’ turnout gear
- Rehydration and replenishment of electrolytes through drinking water and sports drinks
- Treat hyperthermia with passive or active cooling (i.e.-wet towels applied to the neck or forearm immersion in cold water).
- Treat hypothermia with passive or active rewarming (i.e.-removal of wet/cold clothing, place firefighter in warm environment, cover with blankets).
- For moderate to severe dehydration, consider intravenous fluid administration (if equipped).
- Nourishment: calorie replenishment through good carbohydrates (fruit, granola bars). Avoid the following: carbonated beverages, caffeine, fast food, and any foods that are high in fat.
- Always have a dedicated ambulance available for transport to the emergency room.
The importance of firefighter rehabilitation cannot be overemphasized. It is as integral to incident mitigation and safety as fire attack, establishing water supply, R.I.C. or any other fireground role.
Do you have any tips for performing rehab at your fire department? Please leave them in the comments section below.
Photos courtesy of Brett Dzadik and Jim Moss











For rehydration, you should keep a stock of WHO standard oral rehydration salts on hand. 30g sachets to be mixed with 1L of water can be had for 55 cents a packet or less in bulk quantities. Jianas Brothers is one brand available on the web that’s not as overpriced and overcommercialized as some of the more consumer-oriented brands, where you might pay $7 a packet. See here: https://rehydrate.org/resources/jianas.htm
Commercial sports drinks are mostly liquid junk food designed to sell, not for optimal rehydration, and IV rehydration is much more dangerous and should only be used when really necessary.